Application of Deep Learning in Remote Sensing Monitoring of Large Herbivores- A Case Study in Qinghai Tibet Plateau
Application of Deep Learning in Remote Sensing Monitoring of Large Herbivores- A Case Study in Qinghai Tibet Plateau
Wei Luo 1,2,3, Yongtao Jin 1,2,3, Xuqing Li 1,2,3 and Ke Liu 1,2,3*
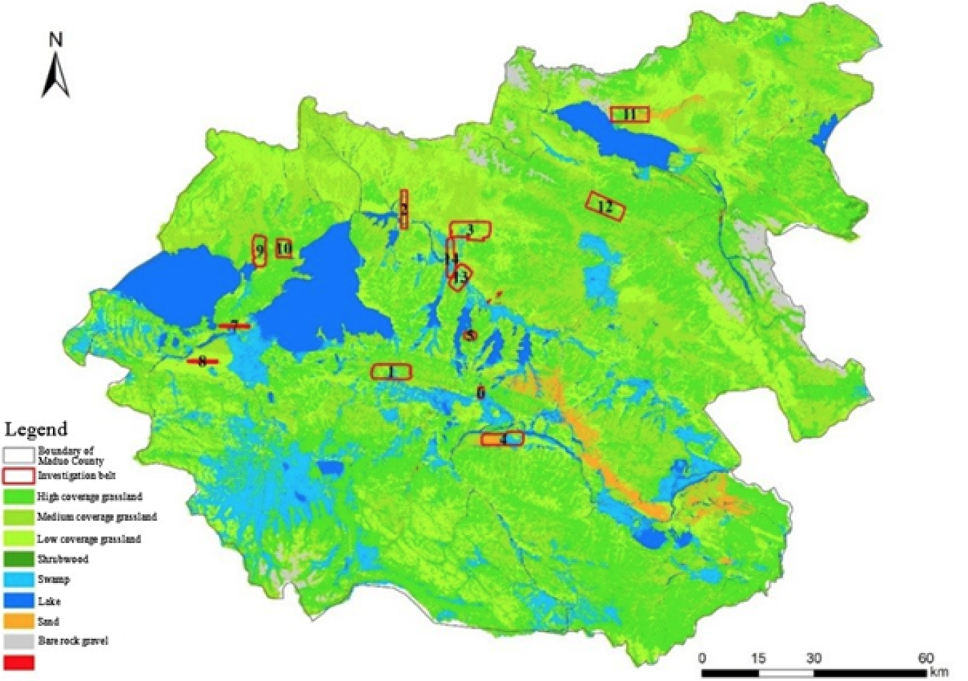
Track and identifier of the UAV investigation of large herbivorous in Maduo County.
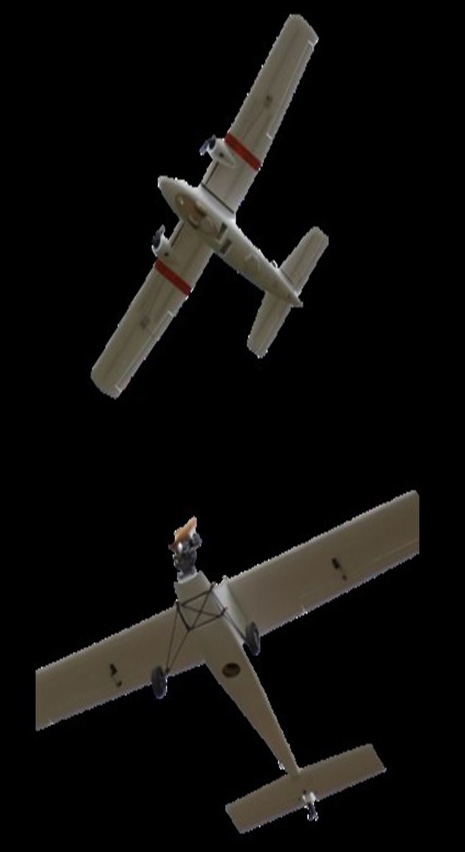
UAVs used for this aerial photography: electric fixed wing UAV (a) and oil powered fixed wing UAV (b).
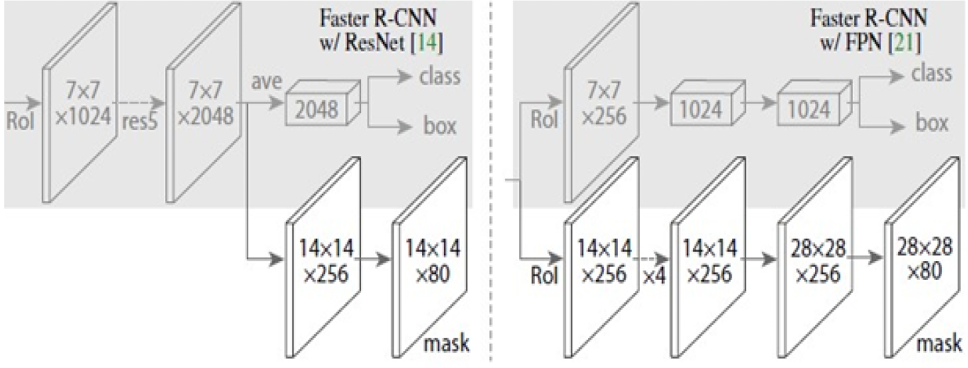
Mask R-CNN structure.
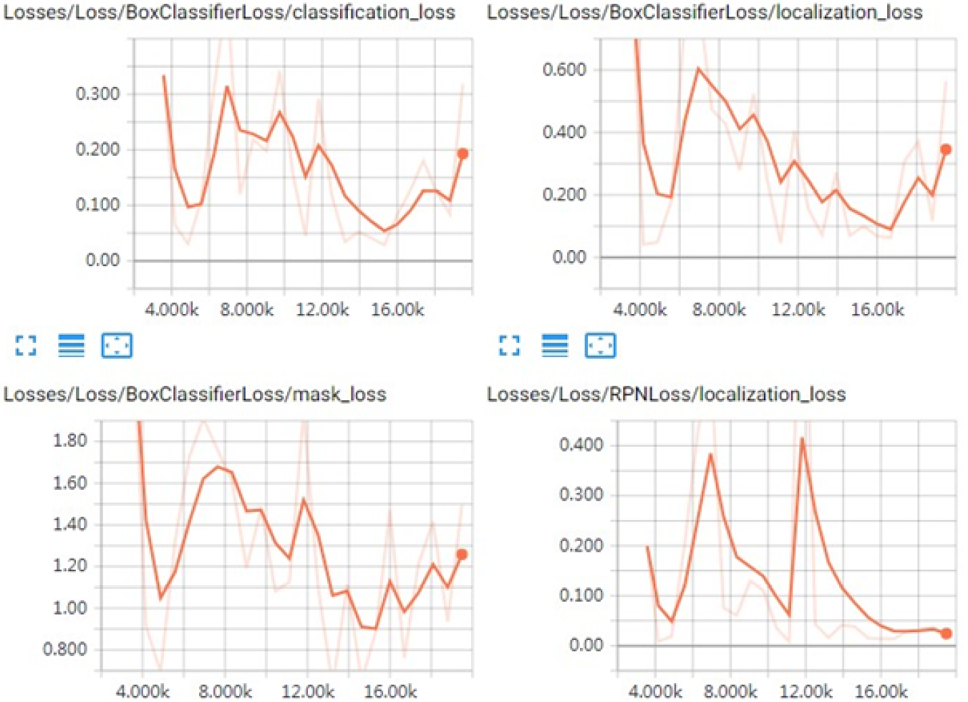
Loss curves generated during the detection process.
Results of the detection and location of herbivores: Domestic Yak (a), Tibetan sheep (b), horse (c), Tibetan wild ass (d), Tibetan gazelle (e), and Blue sheep (f).
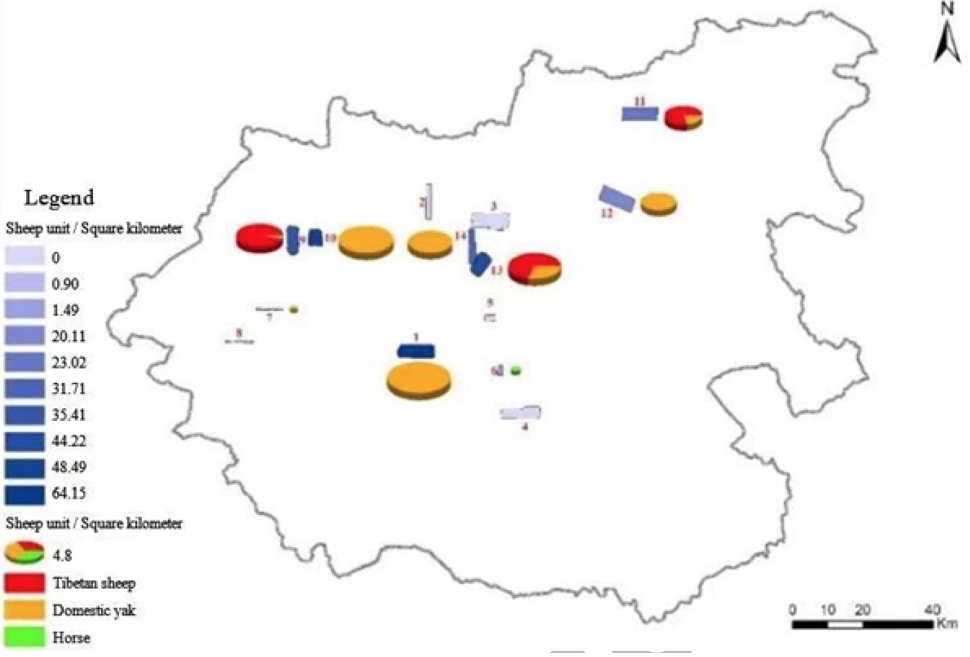
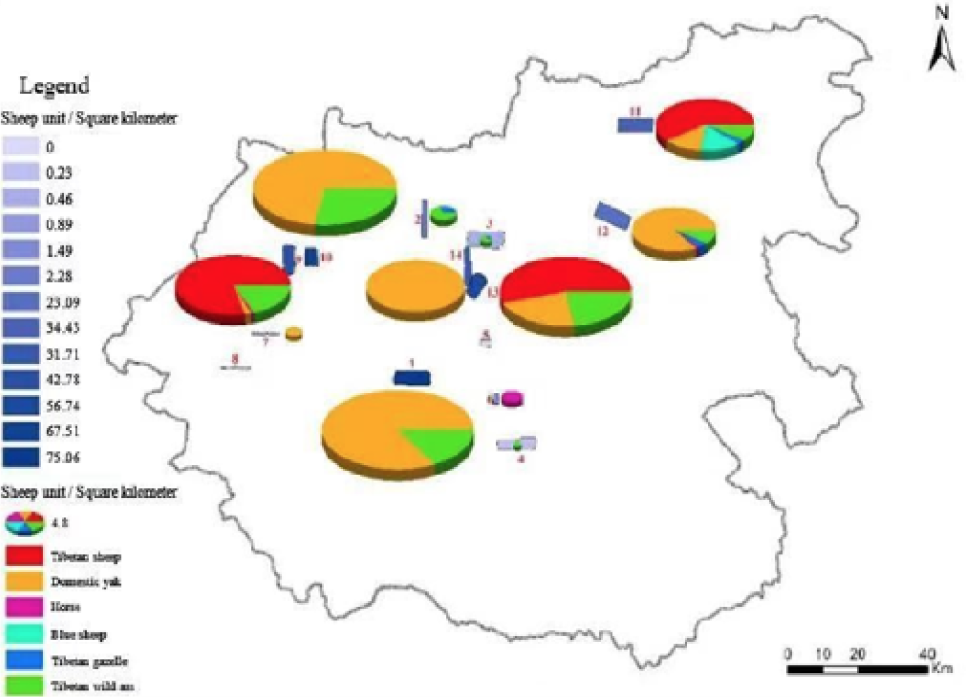
Density distribution of domestic herbivores investigation belt in various zones.
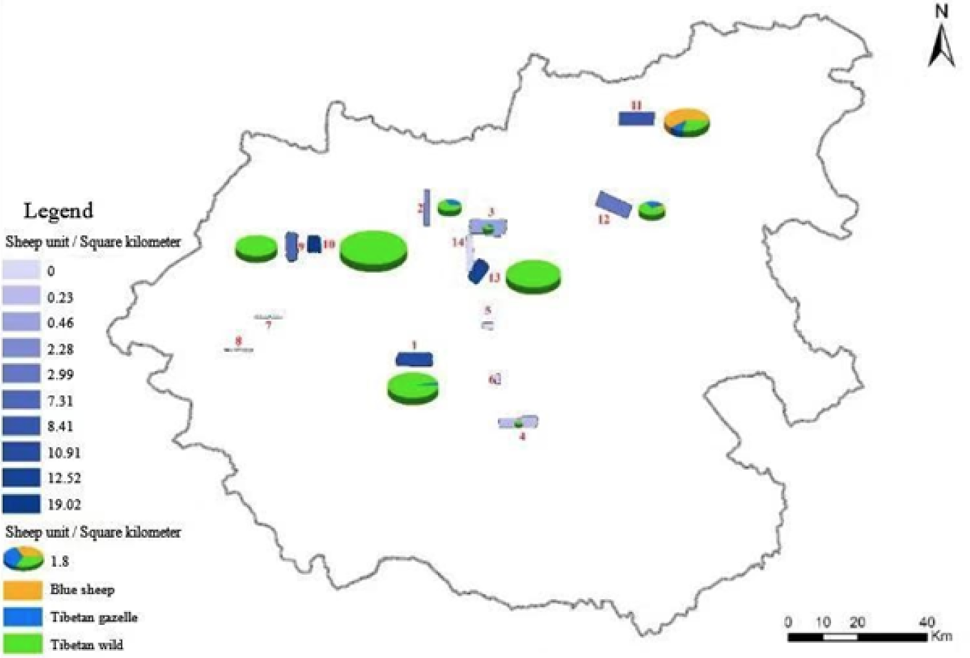
Density distribution of wild herbivores investigation belt in various zones.
Density distribution of large herbivores investigation belt in various zones.
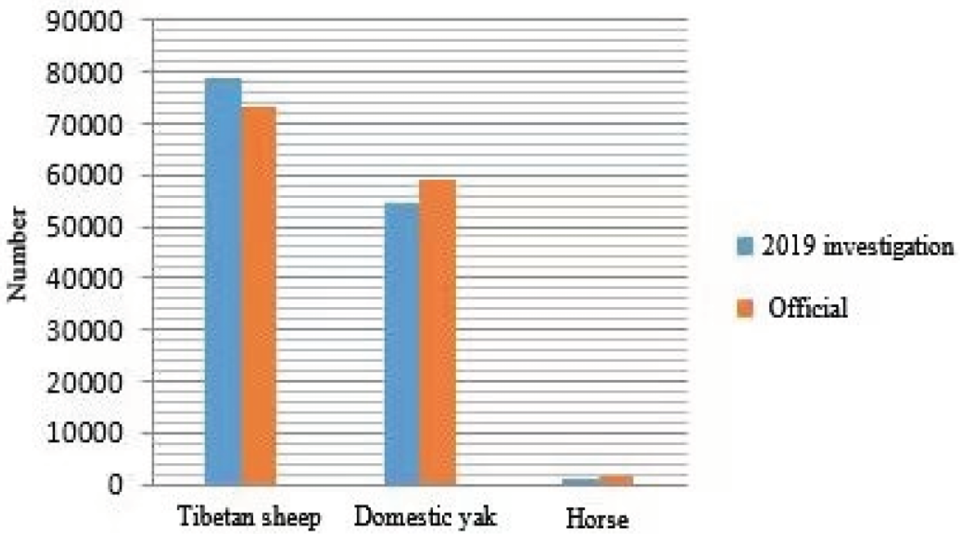
Comparison of the number of domestic herbivores on hand between UAV investigation and official provide.