Habitat Evaluation for Reintroduced Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) in Dongzhai National Nature Reserve, China, Based on a Maximum Entropy Model
Habitat Evaluation for Reintroduced Crested Ibis (Nipponia nippon) in Dongzhai National Nature Reserve, China, Based on a Maximum Entropy Model
Liumeng Zheng1, Yanmei Wang1, Jiagui Zhu2, Ke Wang2, Dejing Cai2, Yuanzhao Qin3, Yuming Guo3, Hongxing Niu1,* and Yanzhen Bu1,*
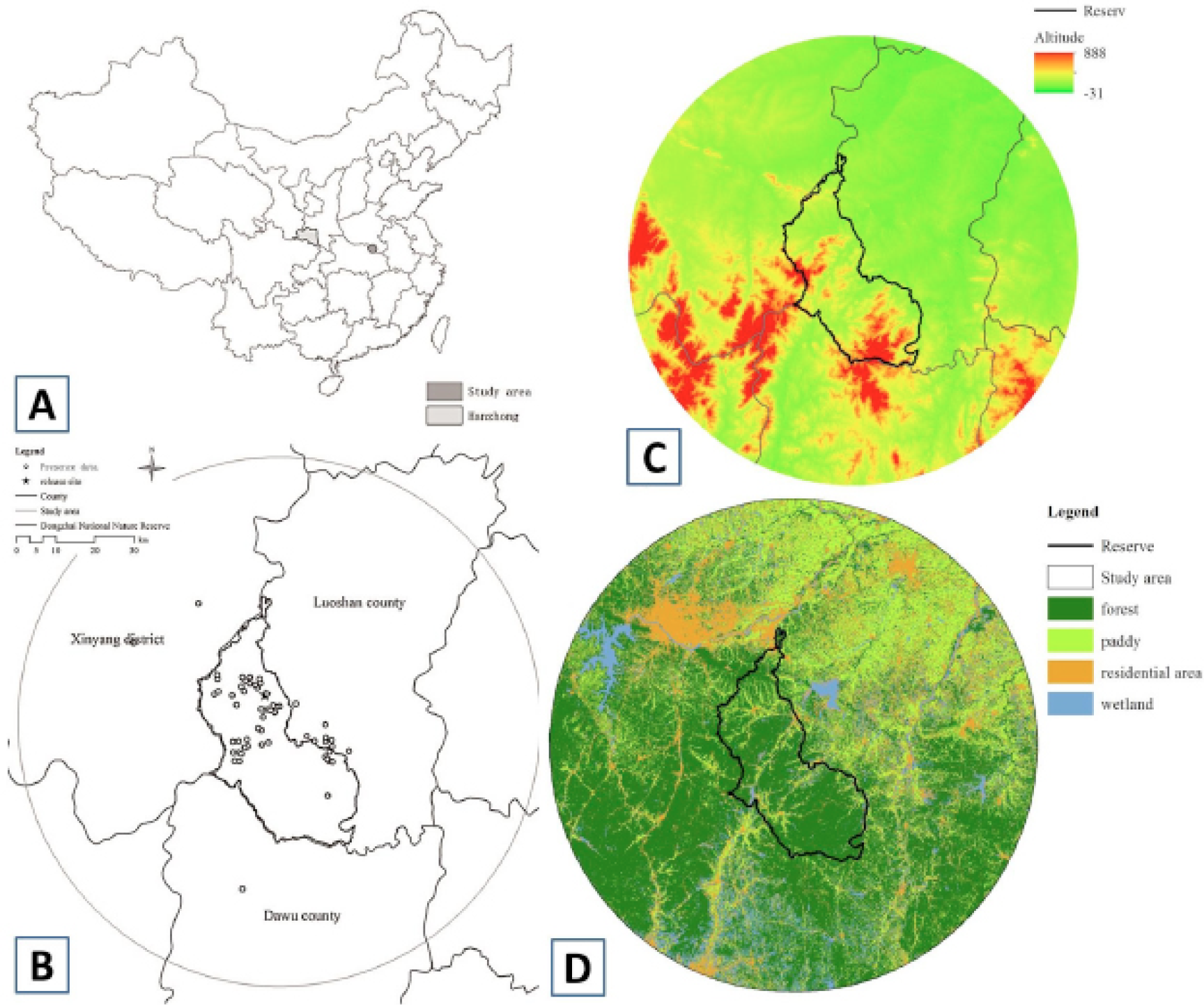
Study area: A, the mainly distribution area of wild crested ibis in Qinling Mountain, Shaanxi Province, and the study area of reintroduction population in Dabie Mountain; B, the dispersal and habitat evaluation area of reintroduced crested ibis in Dongzhai National Nature Reserve; C, the elevation of study area; D, the land cover of the study area.
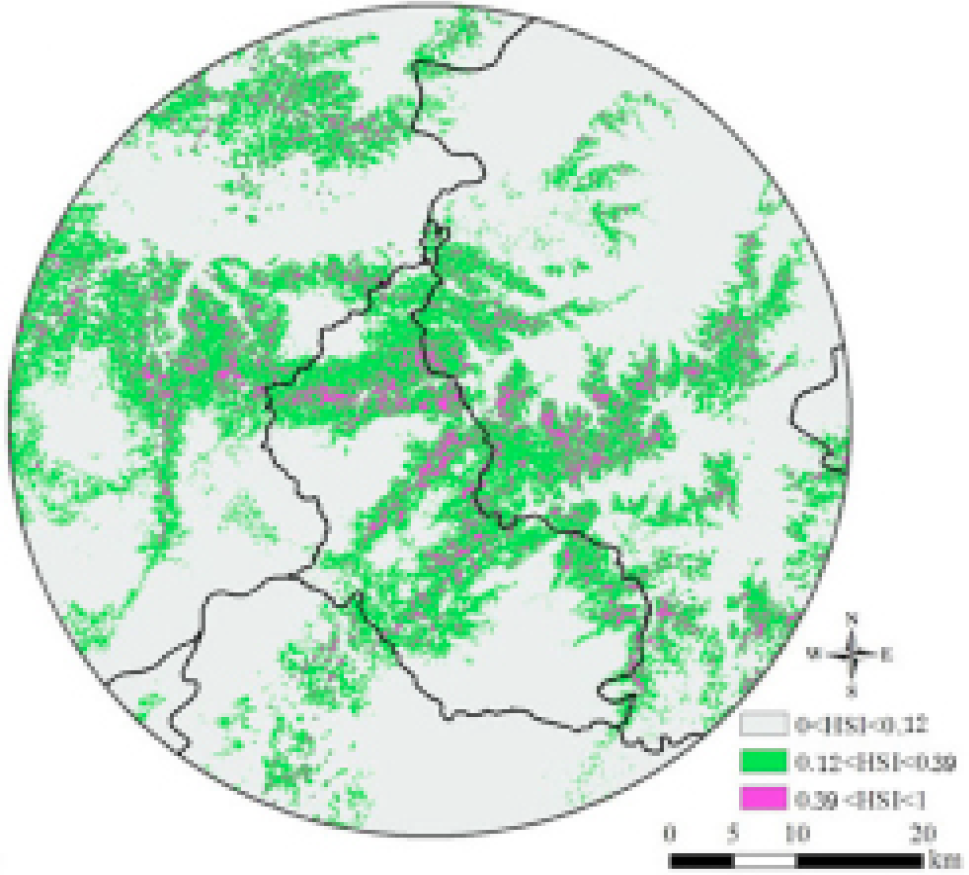
Habitat suitability map for crested ibis. The map of suitable habitat distribution is divided into three classes: least suitable (0 < HIS < 0.12), moderately suitable (0.12 < HIS < 0.39), and most suitable (0.39 < HIS < 1).
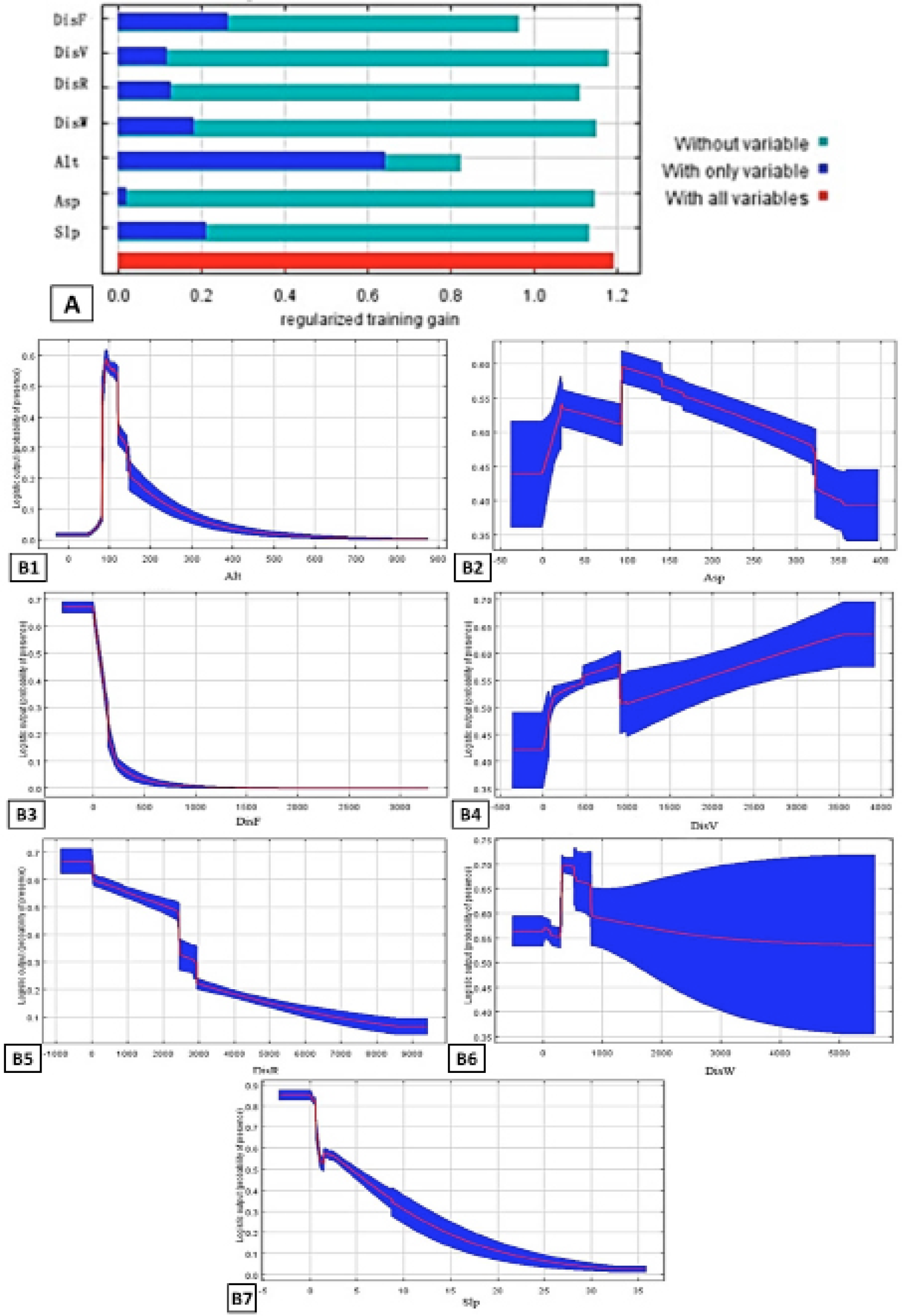
Results of MaxEnt models: A, Jackknife test of variable importance. Codes of the variables are shown in Table I; B, relationship between main environmental variables and habitat suitability for crested ibis.