Novel SNP Markers for Non-invasive Samples in Tibetan Macaque (Macaca thibetana)
Novel SNP Markers for Non-invasive Samples in Tibetan Macaque (Macaca thibetana)
Hua Liu, Wei Hou, Li Peng, Changjun Peng, Yansen Cai and Jing Li*
The distribution of our sampling sites.
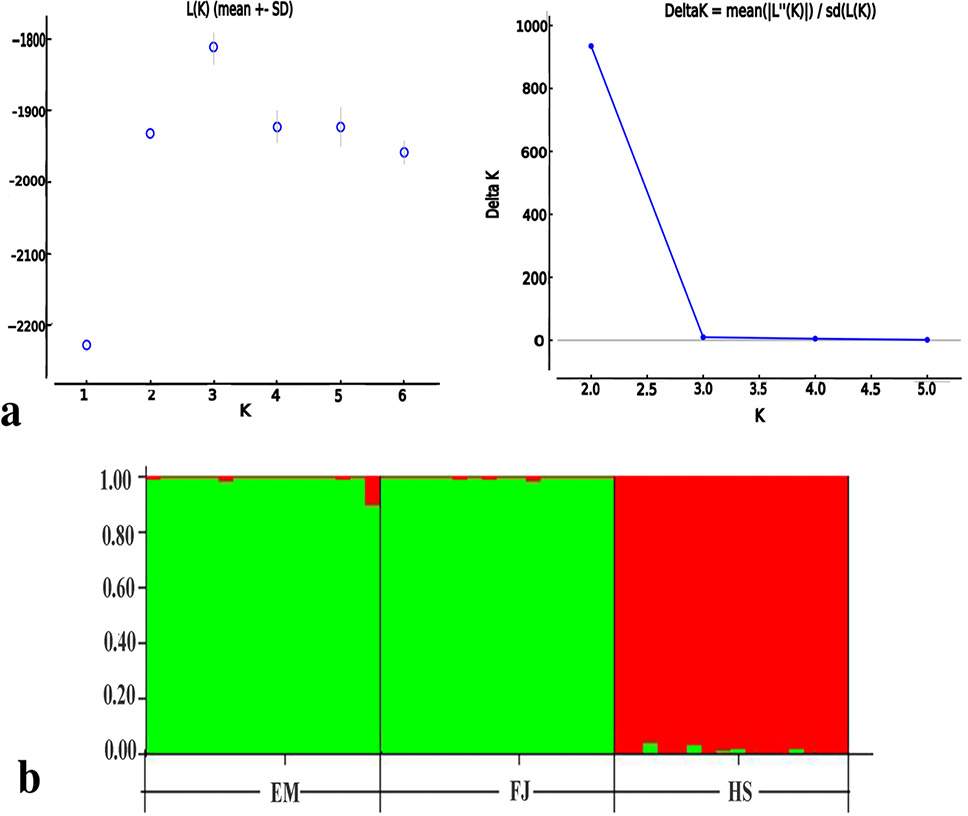
Genetic structure analysis of M. thibetana based on 26 SNP loci. (a) Estimation number of genetic clusters (K) from 10 independent runs for K=1-6. The left panel shows the rate of change (ΔK). The right panel shows the mean of test Ln probability of data. K=2 shows the most posterior probabilities of the K values (b) The colors indicated the likely proportion of inferred clusters that each individual may assigned to. The EM and FJ individuals were assigned the similar genetic clusters, while HS individuals assigned the other distinct cluster. The sampling areas of the individuals are shown at the bottom. HS, Husangshan-Yulinkeng; EM, Emei mountain-Shengtai houqu; FJ, Fanjingshan-huilongwan.
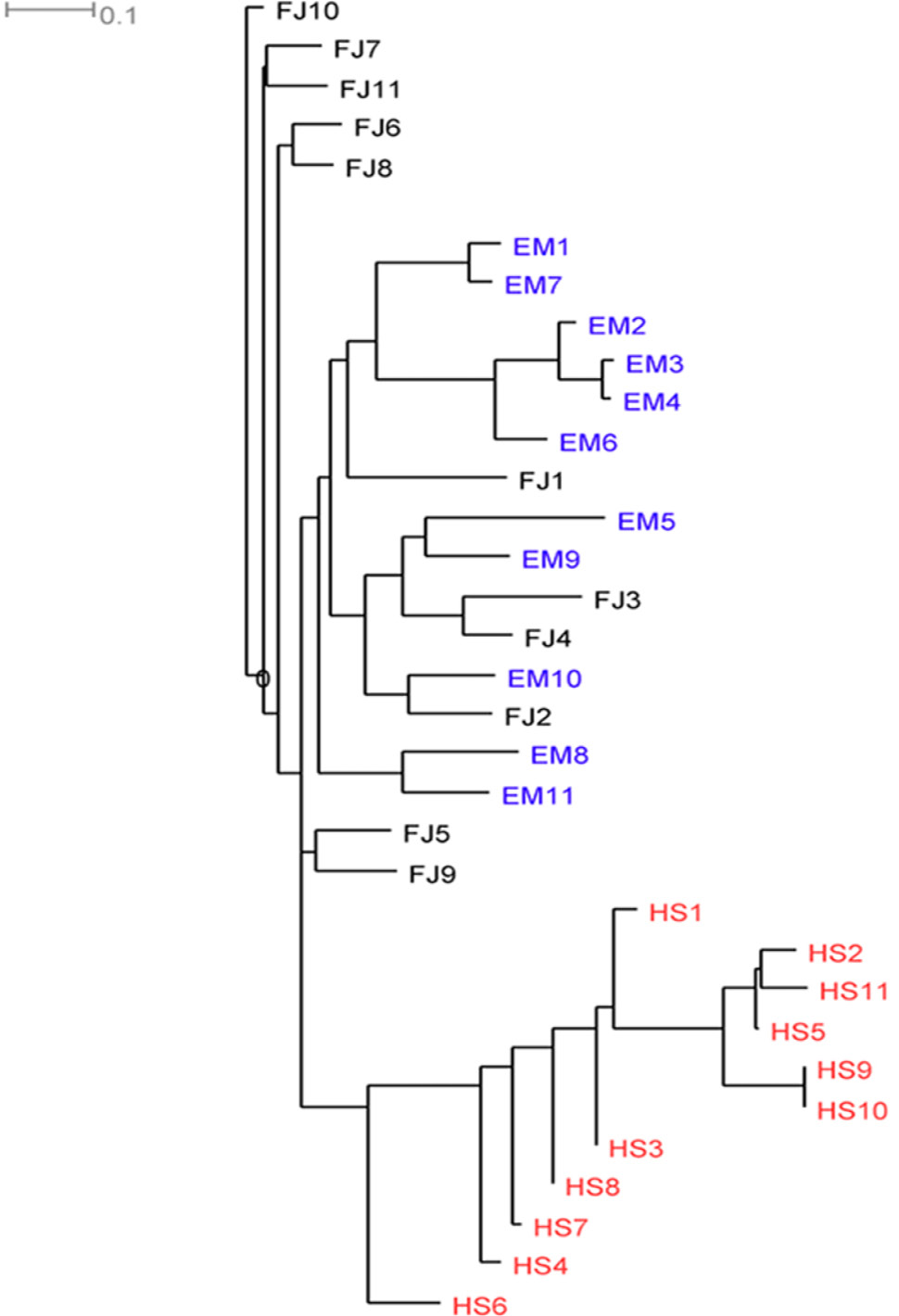
Neighbour-joining tree of 33 M. thibetana individuals constructed based on 26 SNP loci. The color of samples were associated with the geographical origins. HS, Husangshan-Yulinkeng; EM, Emei mountain-Shengtai houqu; FJ, Fanjingshan-huilongwan.
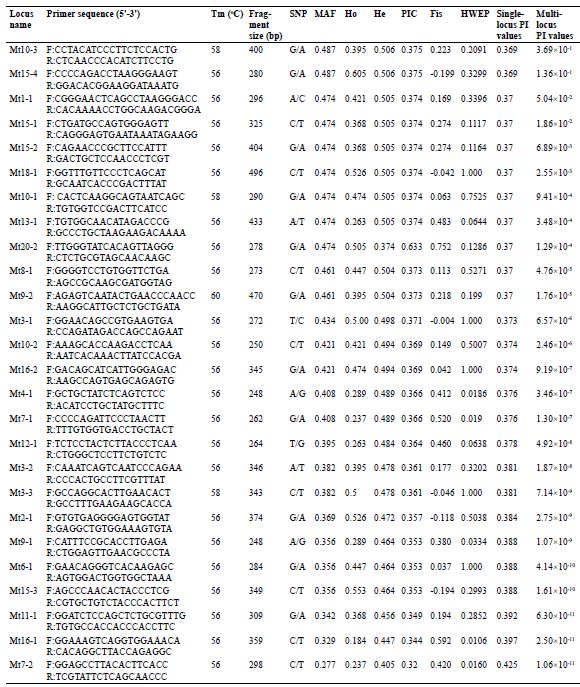
Identification and characteristics of 26 novel SNP loci in 38 individuals of M. thibetana.