Effect of High Dietary Consumption of Locally Available Ghee on Renal Function in Mice
Effect of High Dietary Consumption of Locally Available Ghee on Renal Function in Mice
Dilara Abbas Bukhari*, Mehwish Faheem, Shamoona Arshad and Khalid P. Lone
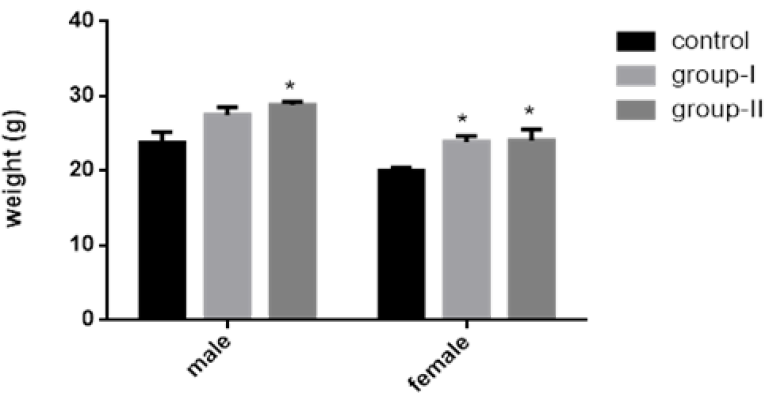
Average weight gain in control and experimental groups fed with normal mice chow and experimental diets respectively. Data expressed as mean ± S.E.M. *=P<0.05.
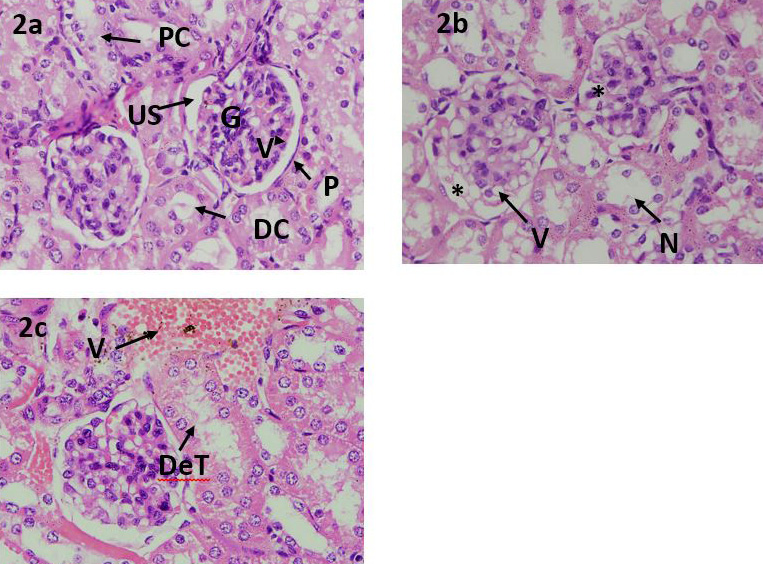
(A) Photomicrograph of mice kidney from control group. PCT: proximal convoluted tubules; G: glomerulus; VL: visceral layer; PL: parietal layer; US; urinary space; DCT: distal convoluted tubules, (B & C) Photomicrograph of mice kidney fed with experimental diets. V: vacuolization; N: necrosis; DeT: degenerated tubules; VC: vascular congestion.
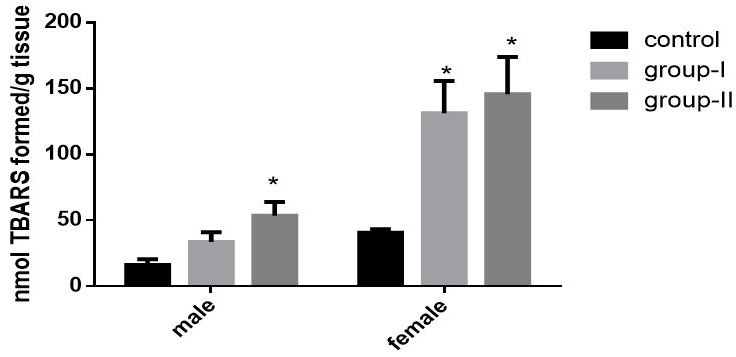
Lipid peroxidation in mice kidney fed with 10% of ghee for 4 weeks. The values given are mean ± S.E.M.
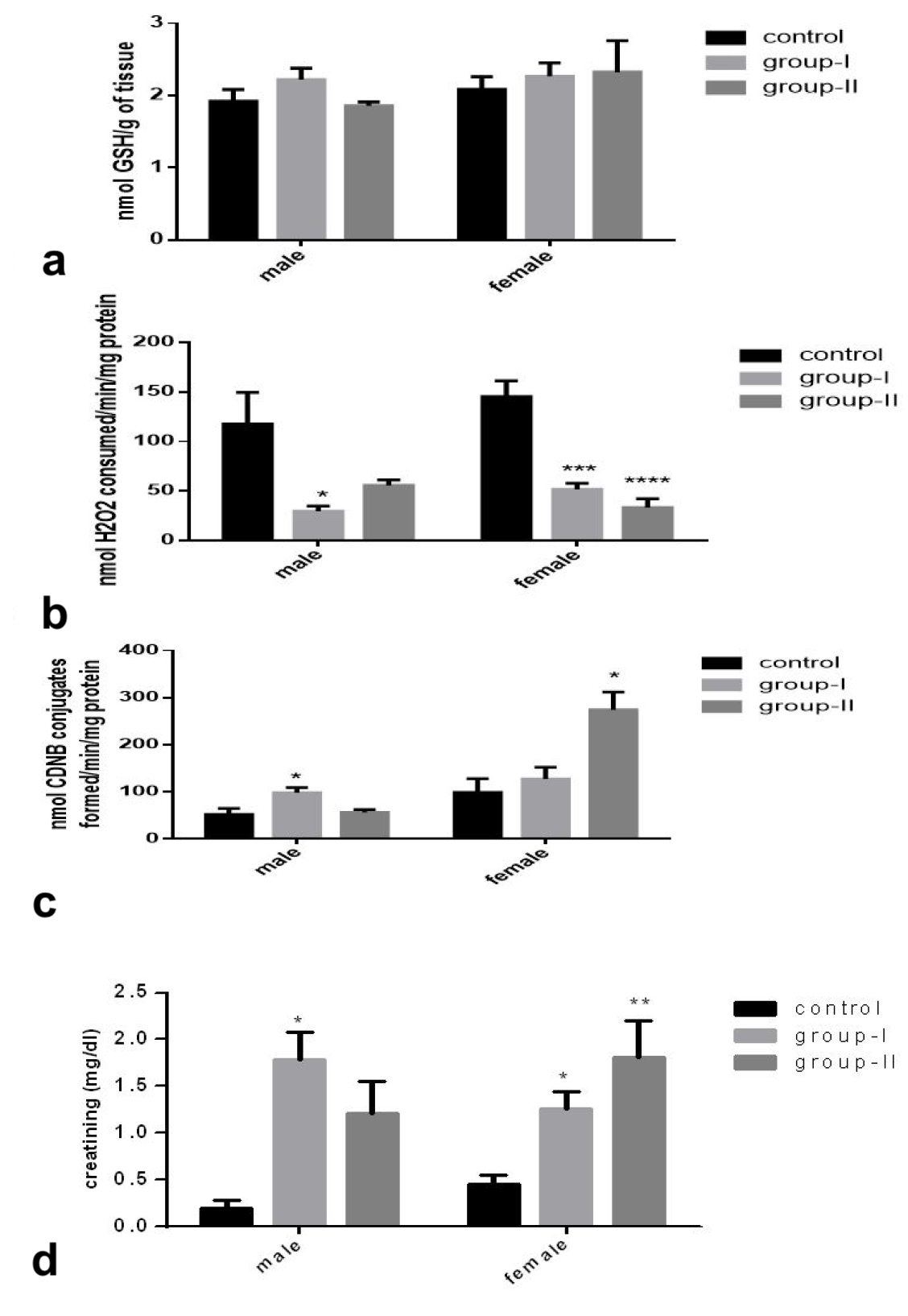
(a) Glutathione level, (b) Catalase activity, (c) Glutathione-S-transferase activity and (d) Creatinine level in mice kidney fed with 10% of ghee for 4 weeks. The values given are mean ± S.E.M.