In-vivo Evaluation of Anti-urolithiatic Activity of Different Extracts of Peel and Pulp of Cucumis melo L. in Mice Model of Kidney Stone Formation
In-vivo Evaluation of Anti-urolithiatic Activity of Different Extracts of Peel and Pulp of Cucumis melo L. in Mice Model of Kidney Stone Formation
Aneeqa Saleem1, Muhammad Islam1, Hamid Saeed1* and Mehwish Iqtedar2
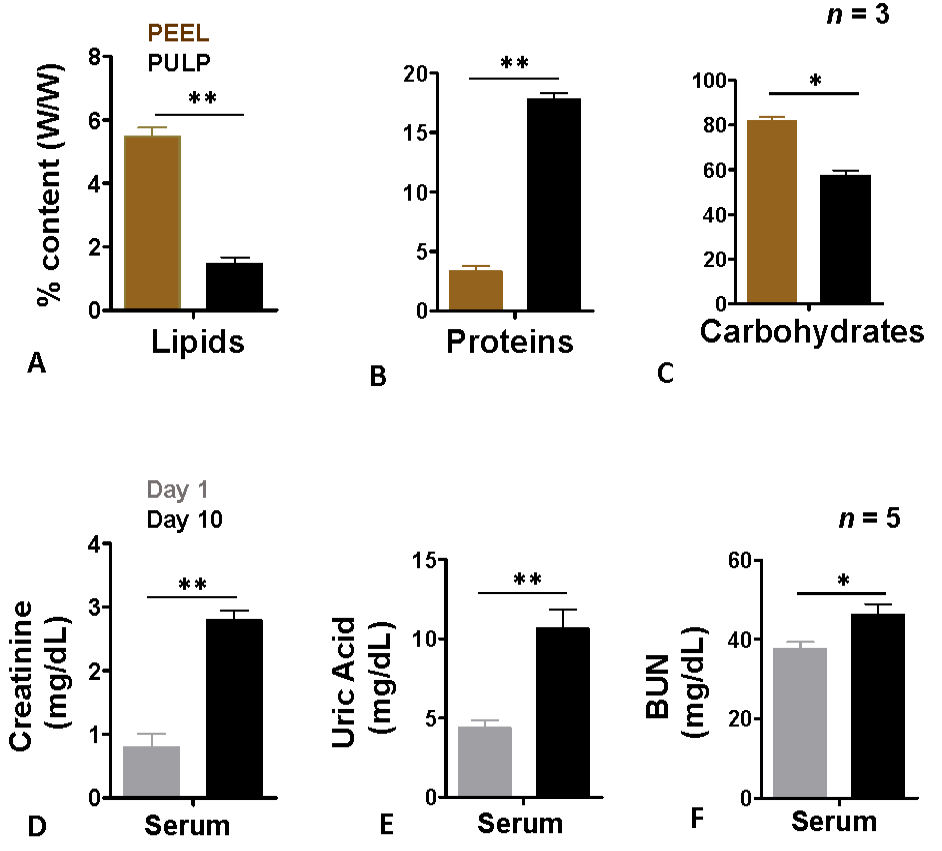
Primary metabolites in Cucumis melo L. and establishment of mice model of kidney stone formation. Lipids (A), proteins (B) and carbohydrates (C) in peel (brown bars) and pulp (black bars) of Cucumis melo L. serum creatinine (D), uric acid (E) and BUN (blood urea nitrogen) (mg/dL) (F) levels at day1 (grey bars) and day 10 (black bars) after intraperitoneal injections of ethylene glycol (0.75% V/V).
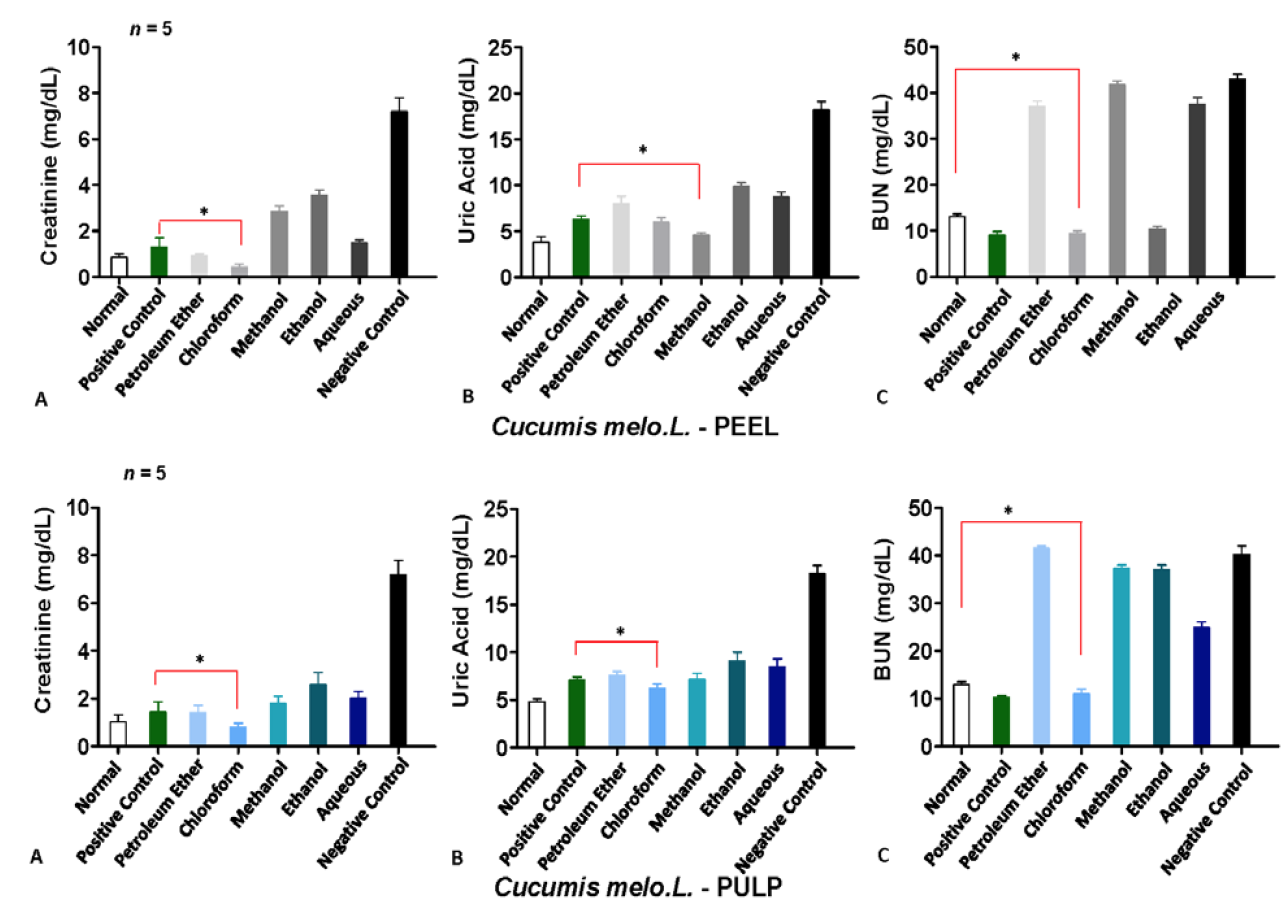
Anti-urolithiatic activity of extracts of peel and pulp of Cucumis melo L. Serum creatinine levels (mg/dL) (A), serum uric acid levels (mg/dL) (B) and serum BUN levels (mg/dL) (C). White bars represent normal samples, green bars represent positive control and black bars represent negative control. * indicates p-values of ≤ 0.05.