Molecular Cloning and Expression Analysis of Vps26A Gene from Deer Antler Tip of Different Growth Stages
Molecular Cloning and Expression Analysis of Vps26A Gene from Deer Antler Tip of Different Growth Stages
Yanling Xia1,2, Heping Li2, Yuntao Liang2, Jichen Zhao2, Binshan Lu2 and Di Liu1,*
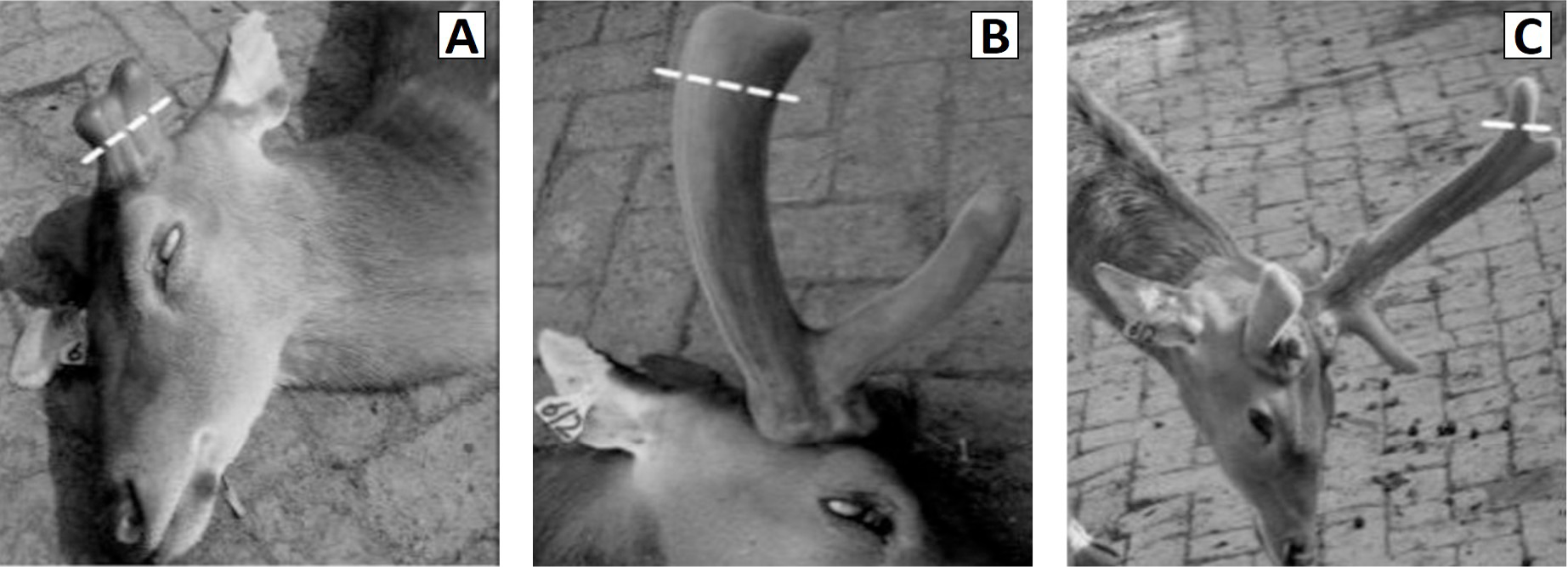
Deer antlers from different growth periods. A, deer antler of 30 days; B, deer antler of 60 days; C, deer antler of 90 days.
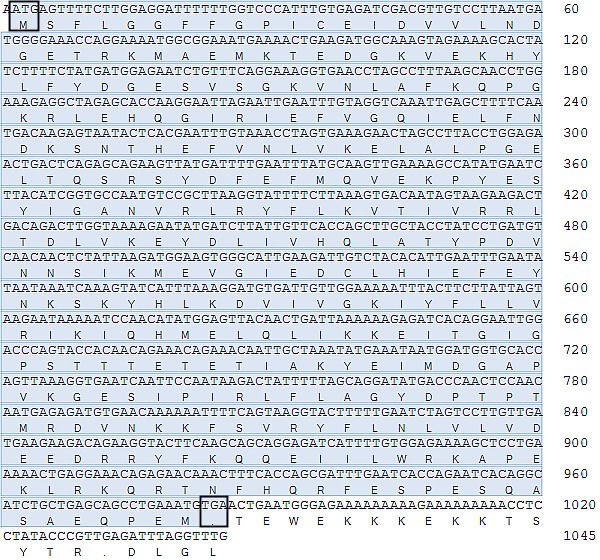
Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of Vps26A cDNA from sika deer (ATG is the initiation codon; * is the stop codon).
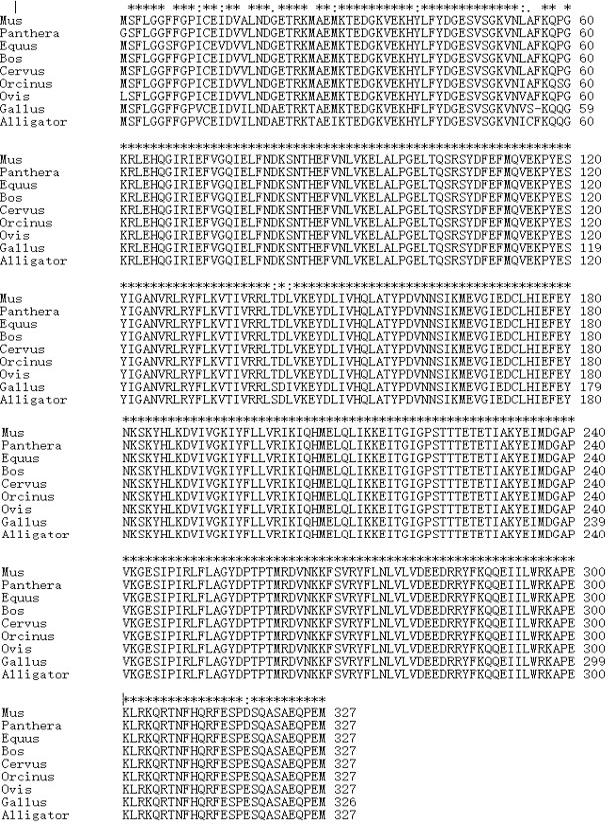
Multiple alignment of Vps26A protein sequences from different species.
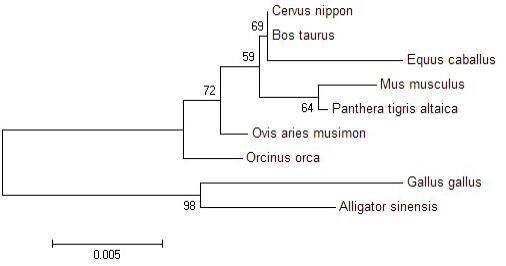
The phylogenetic tree of Vps26A proteins from different species. Phylogenetic analysis based on the Vps26A amino acid sequences from various animals. The phylogenic tree for the Vps26A proteins was constructed using the neighbor-joining method. The origins and accession numbers of the Vps26A sequences were: Bos taurus (NP_001068923.1); Equus caballus (XP_005613841.1); Mus musculus (NP_598433.1); Panthera tigris altaica (XP_015399148); Ovis aries musimon (XP_011980964.1); Orcinus orca (XP_004280845.1); Alligator sinensis (XP_006023201.1); Gallus gallus (XP_421577.2).
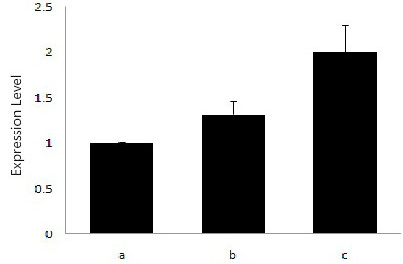
Expression of Vps26A gene in different growth periods from sika deer antler. a, 30 days; b, 60 days; c, 90 days.