Effect of Chitosan on Induced Skin Wound Healing in Rabbits: Histopathological Evaluation
Effect of Chitosan on Induced Skin Wound Healing in Rabbits: Histopathological Evaluation
Falah Mahmood Hameed1*, Asaad Khalaf Talal AL-Shuwaili2, Eman Jawad Jabber3, Mayada Sahib Hassan1
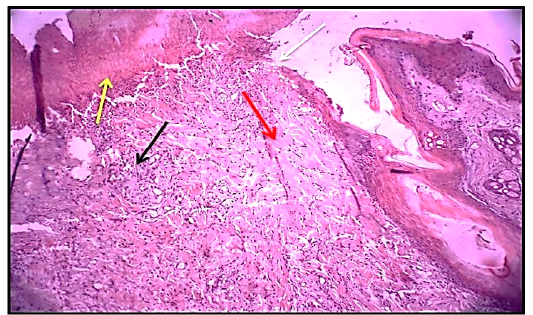
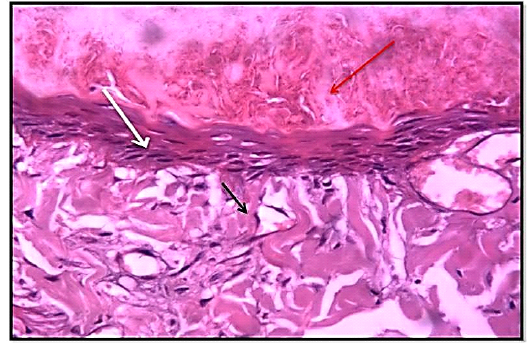
Histological section 3rdday of wound healing control group showed the non – epithelialization surfaces (white arrow), collagen fibers proliferation forming a matrix (red arrow). Granulation tissue formation (black arrow) with the presence of red blood cells (yellow arrow). (Hematoxylin and Eosin ,10 X).
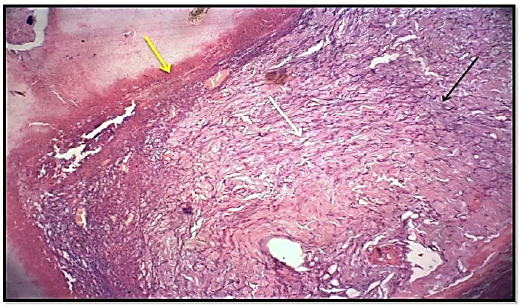
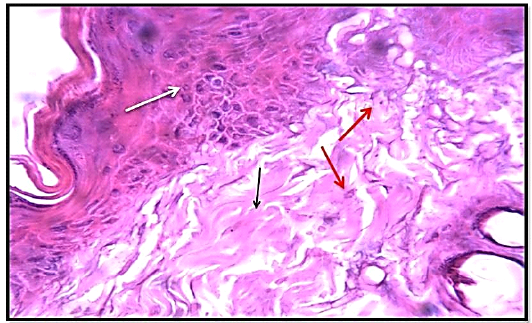
Histological section 3rd day of wound healing for the treated group (locally) showed hemostasis, RBCs (red arrow),mild fibrosis (black arrow) and significant angiogenesis (new emerging blood vessels) (white arrow) Slight granulation tissue. (Hematoxylin and Eosin ,10 X).
Histological section 3rd day of healing in wound for treated group(local, oral) showed slight edema and hemostasis (red arrow), mild fibrosis (collagen fibers) (black arrow) and significant formation of new hair follicles (white arrow) (Hematoxylin and Eosin ,10 X).
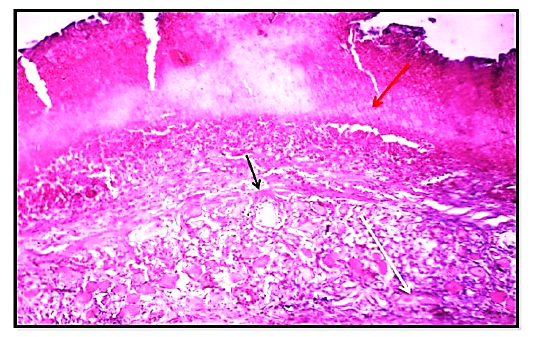
Histological section of wound healing control group at days 7, showed significant highly collagen fibers proliferation ( white arrow). Granulation tissue more cellularity (black arrow) with less presence hemostasis (red blood cells) (yellow arrow). (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 10 X).
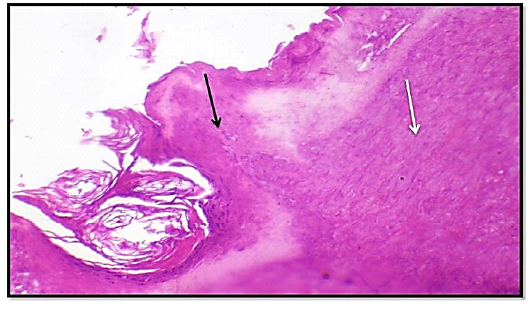
Histological section of 7th day wound healing for treated group (locally) showed hemostasis, edema (red arrow), mild fibrosis and significant numbers of fibrocytes (black arrow) and slight hyperkeratosis (white arrow) slight granulation tissue. (Hematoxylin and Eosin ,10 X).
Histological section of of 7th day healing in wound treated group (locally, orally) showed the slight inflammatory cells infiltration (red arrow), mild fibrosis (collagen fibers) (black arrow) and significant keratocytes proliferation (white arrow). (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 10 X).
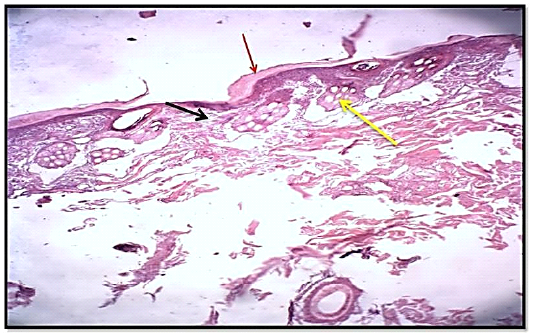
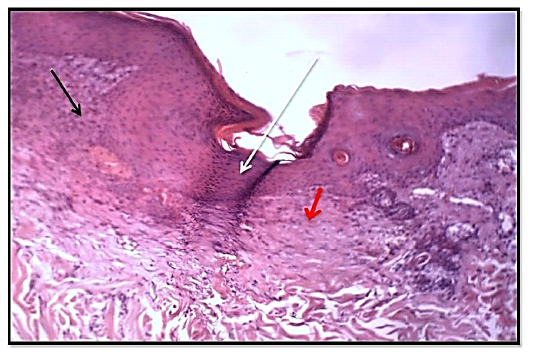
Histological section of 14thday wound healing control group showed the fully epithelized surfaces (white arrow), less collagen fibers proliferation (red arrow). Granulation tissue less cellularity (black arrow) and tissue structure resemble normal. (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 10 X).
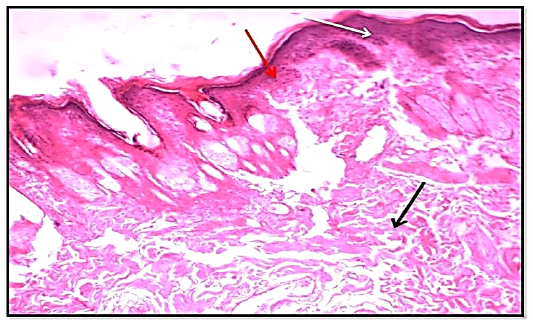
Histological section of 14th day of wound healing treated group (locally) showed re-epithelization (red arrow), mild fibrosis (black arrow) and mild hyperplasia of epidermis (white arrow). slight granulation tissue. (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 10 X).
Histological section of 14thday, of wound healing treated group (locally, orally) showed significant re-epithelialzation in epidermis (black arrow) and extensive granulation tissue formation in dermis (white arrow) (Hematoxylin and Eosin, 10 X).