Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Application for Quantitative Characterization of Edible Grains
Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) Application for Quantitative Characterization of Edible Grains
Saba Iqbal1, Salman Khurshid1*, Hafiza Mehwish Iqbal1, Qurrat-Ul-Ain Akbar1, Aqeel Ahmed Siddique3, Saqib Arif1, Shahid Yousaf2, Masooma Munir4, Abdul Karim Khan4, Shazia Arif5, Abdul Ahad6 and Muhammad Arif7
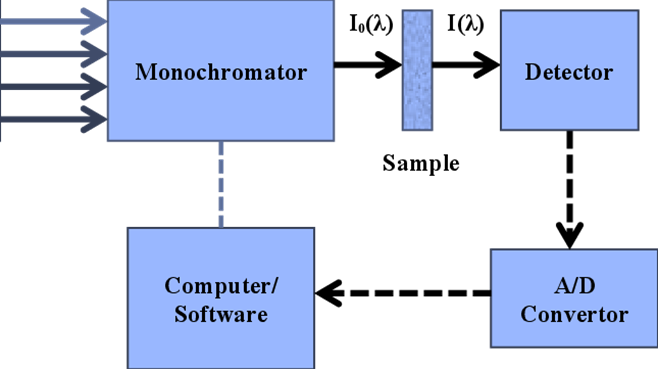
Near infrared spectroscopy schematic diagram.
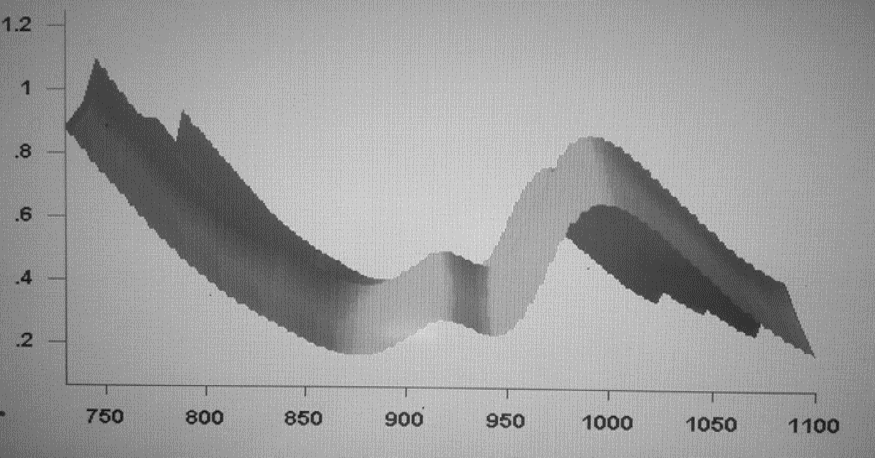
Representative NIR-spectra of wheat hardness.
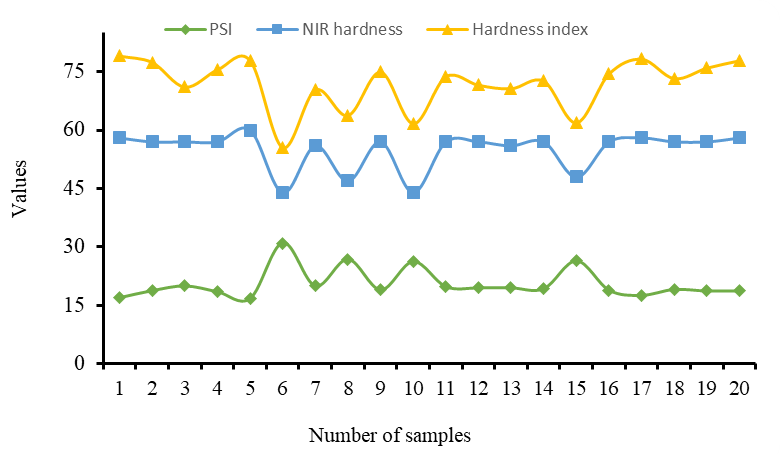
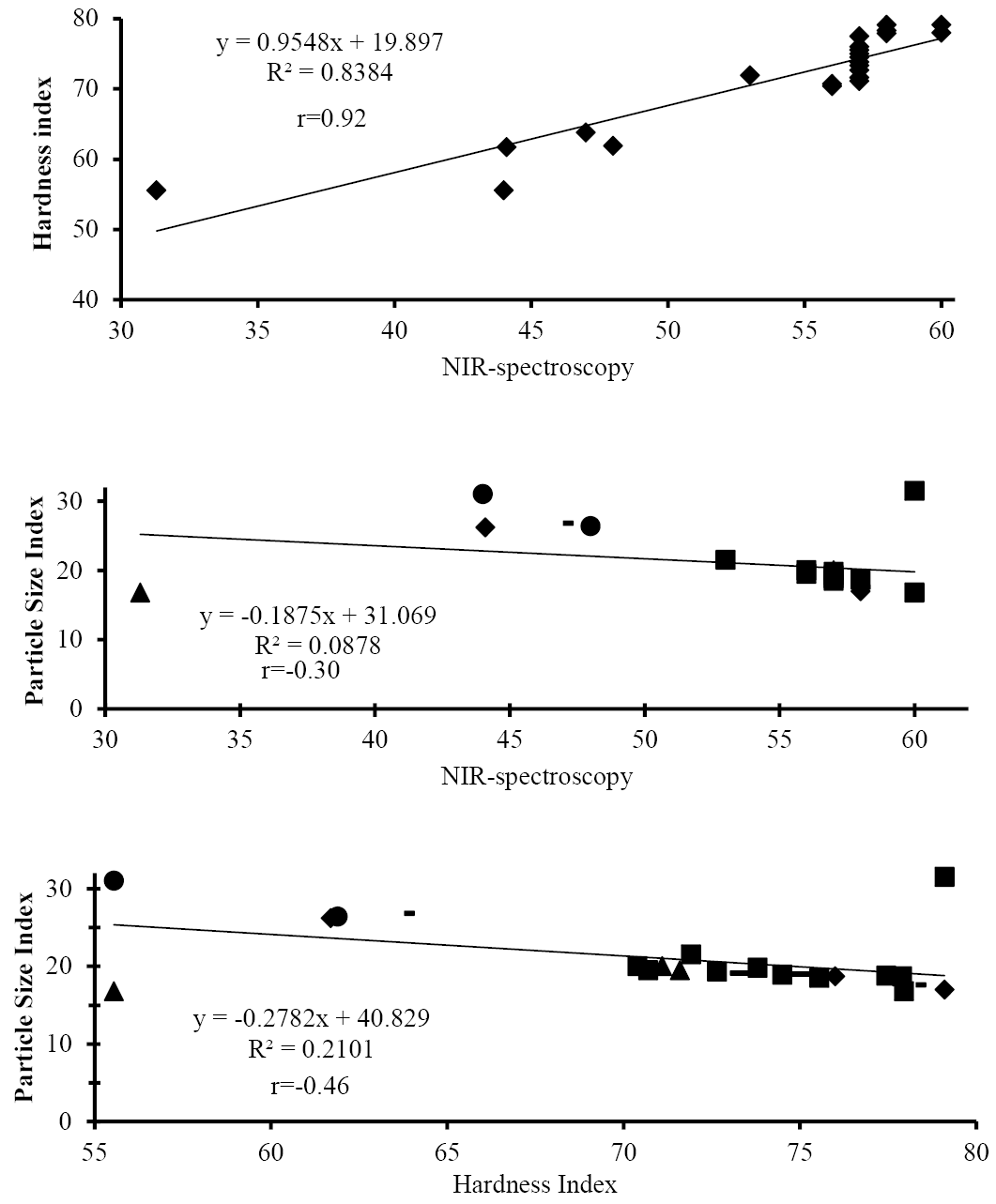
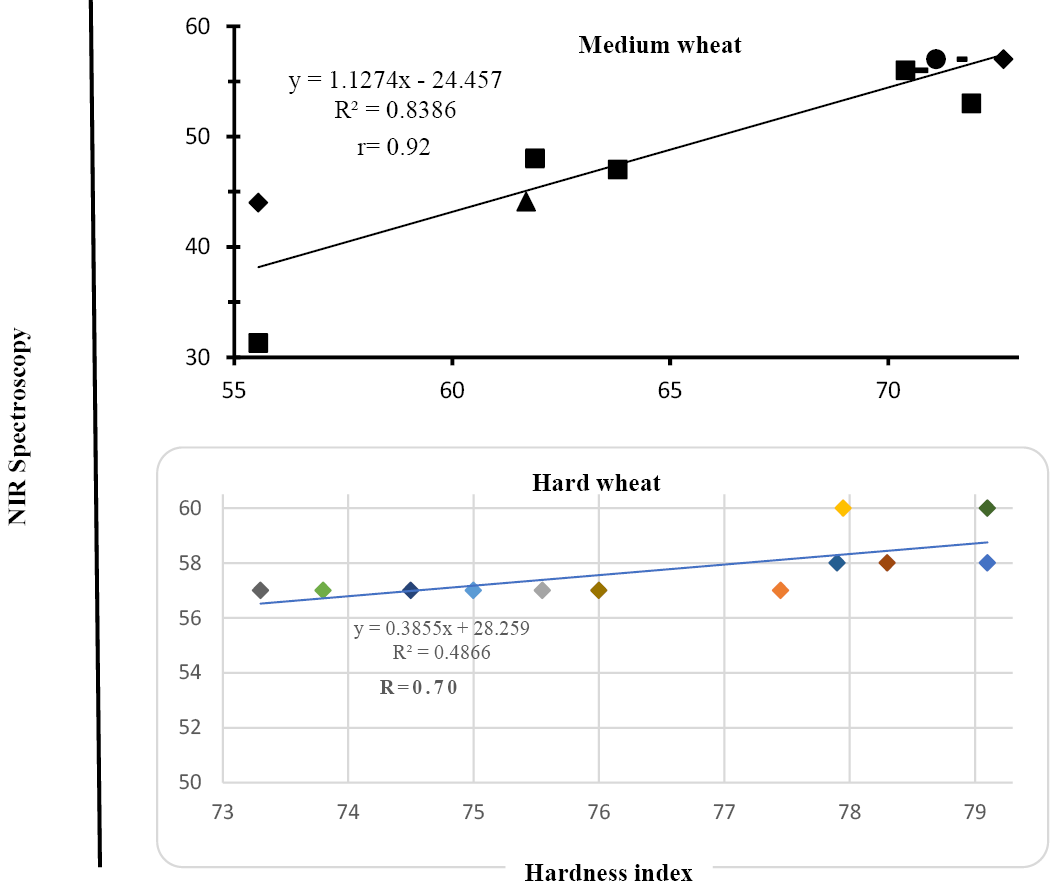
Comparison of near-infrared (NIR) spectrometry with reference methods for hardness of wheat.
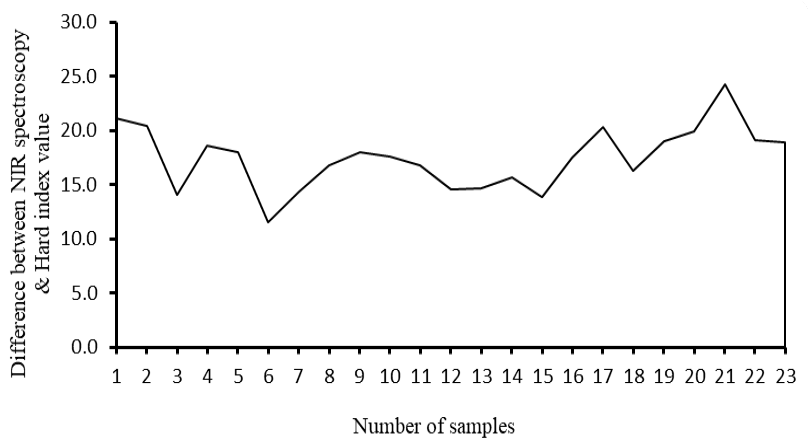
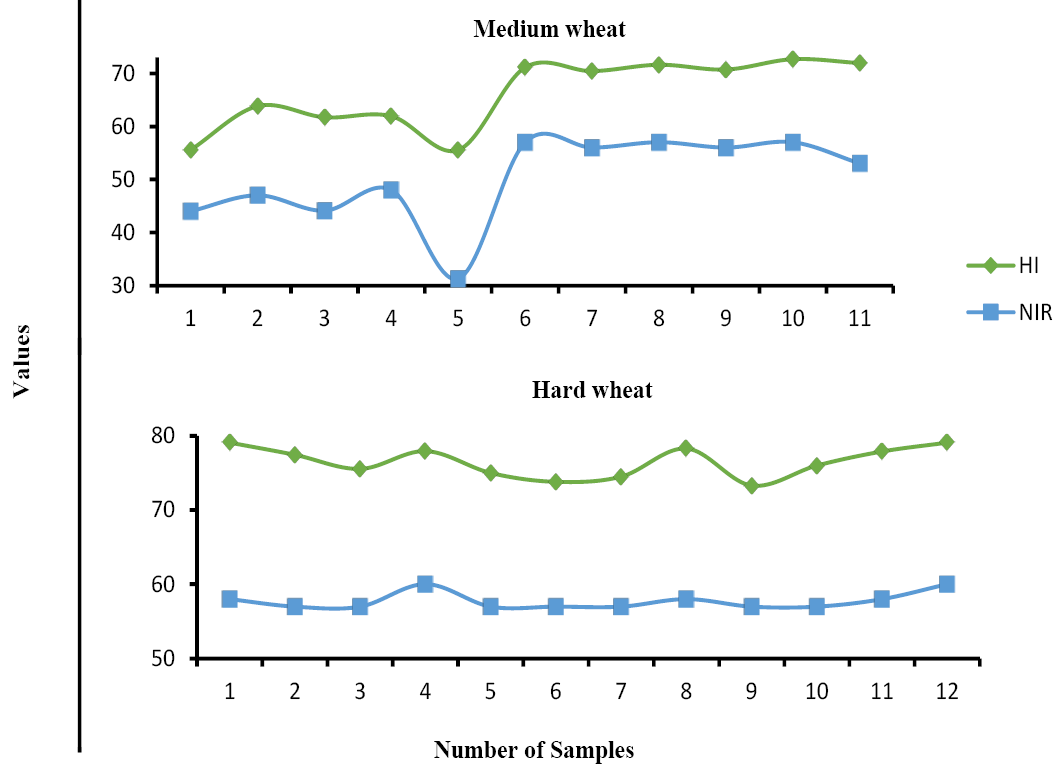
Differences between NIR and hardness index values.
Correlation coefficients (r) between harness values of near-infrared (NIR) spectrometry and reference methods.
Hardness values of medium and hard group of wheat samples.