Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of GPCR, RPO30, P32 and EEV Glycoprotein Genes of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus Recent Isolates in Egypt
Sequencing and Phylogenetic Analysis of GPCR, RPO30, P32 and EEV Glycoprotein Genes of Lumpy Skin Disease Virus Recent Isolates in Egypt
Moustafa A. Zaghloul1*, Mohamed F. Azooz1, Saleh E. Ali1*, Heba M. Soliman1, Maha M. Sayed1, Mohamed H. Kafafy2 and Alaa R. Morsy1
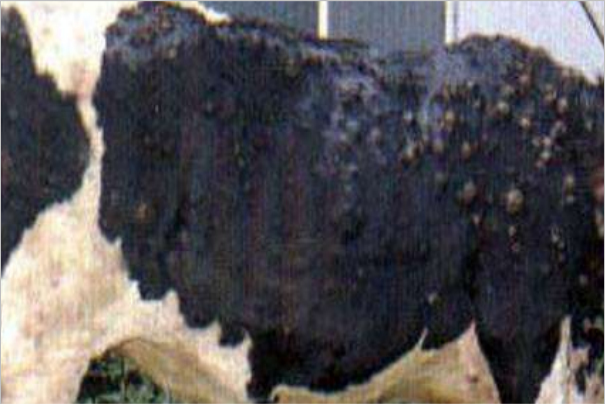
Lumpy skin disease infected animal shows cutaneous nodules covering the entire body.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of LSDV isolates based on the deduced amino acids sequences of 126 EEV proteins showing the genetic relationship between the Egyptian LSDV isolate (LSDA) obtained in this study and other selected LSDV sequences.
Alignment of deduced amino acids of the EEV genes. The Egyptian LSDA isolate was aligned with representative LSDV sequences retrieved from GenBank.
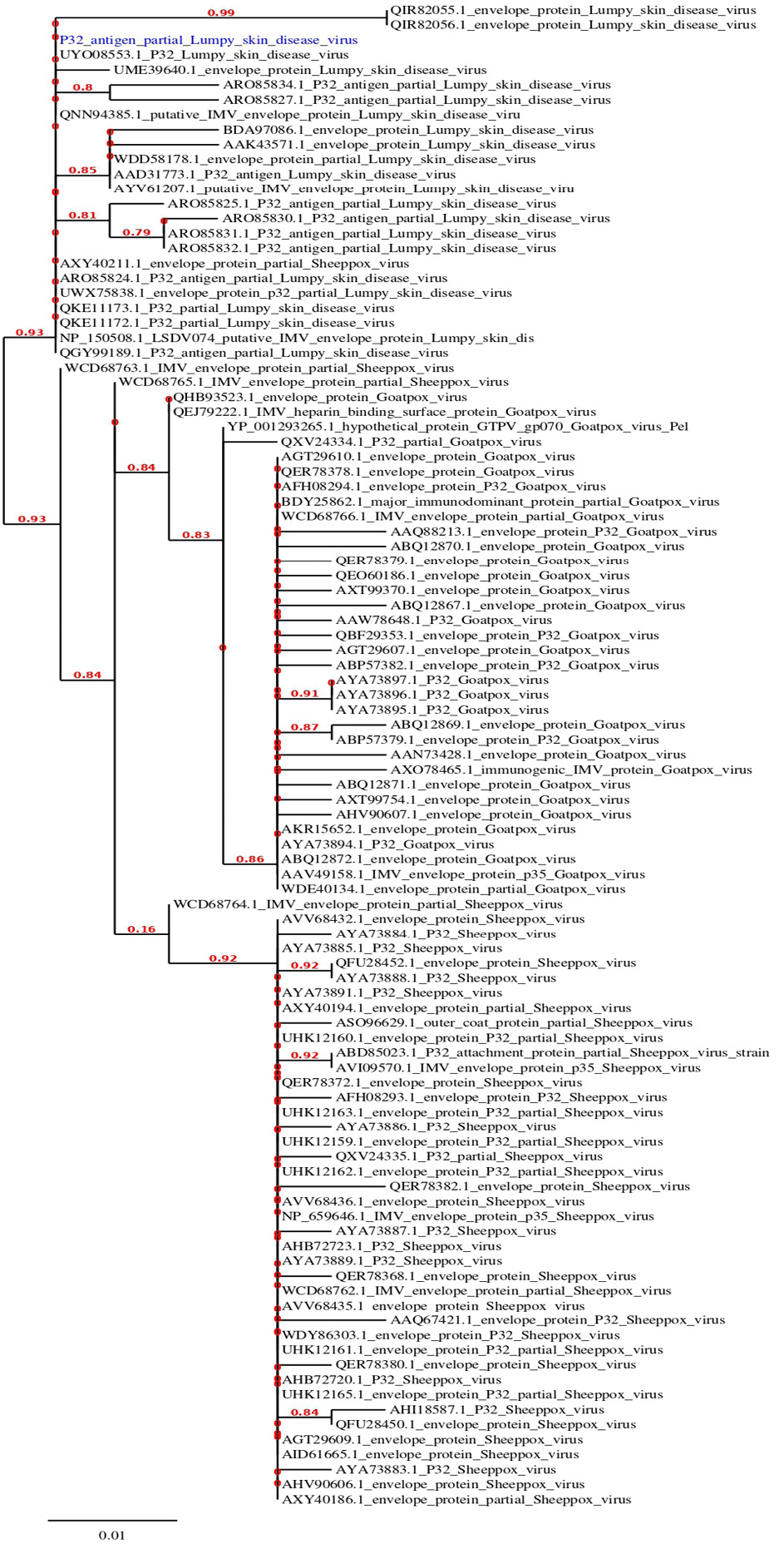
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of LSDA isolate based on the deduced amino acids sequences of P32 protein showing genetic relationship between the Egyptian LSDA isolate obtained in this study and other selected LSDVs.
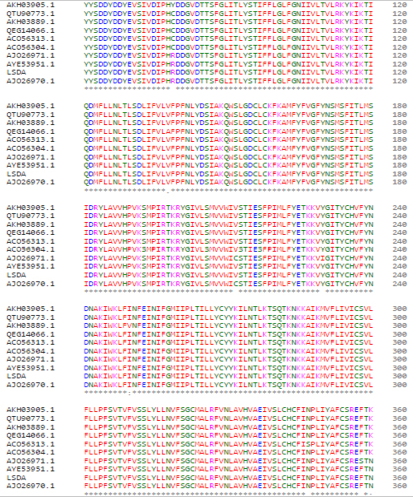
Multiple sequence alignments of deduced amino acids of the P32 gene of LSDV. The Egyptian LSDA isolate was aligned with representative LSDV sequences retrieved from GenBank.
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of LSDA isolate based on the deduced amino acids sequences of G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) protein showing genetic relationship between the Egyptian LSDA isolate obtained in this study and other selected LSDVs.
Multiple sequence alignments of deduced amino acids of the G-protein coupled chemokine receptor (GPCR) gene of LSDA. The Egyptian LSDA isolate was aligned with representative LSDV sequences retrieved from GenBank.
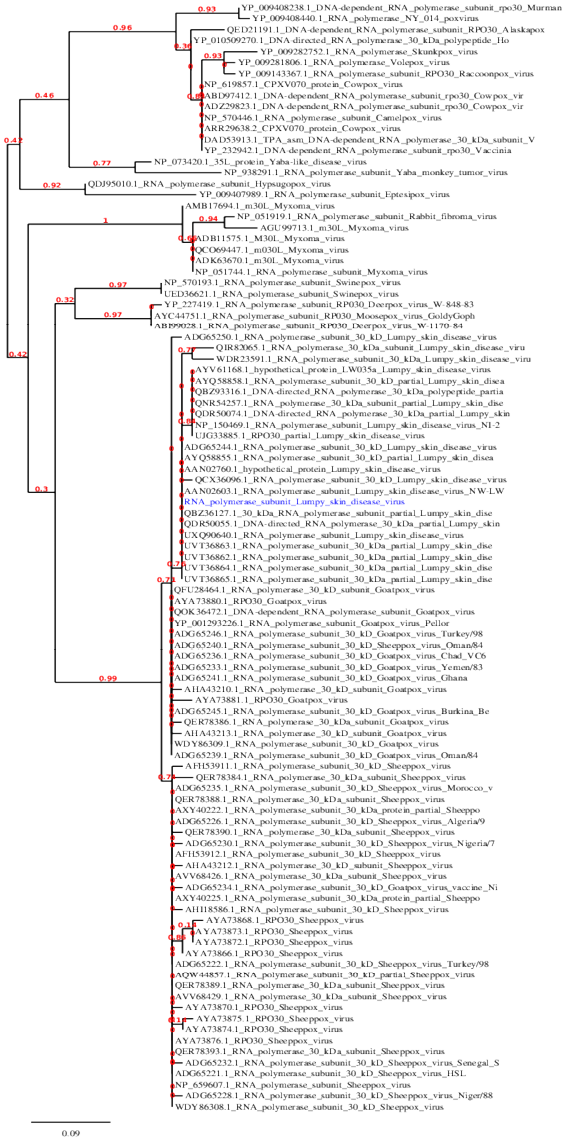
Maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of LSDA isolate based on the deduced amino acids sequences of RNA polymerase subunit 30 kD subunit (RPO30) protein showing genetic relationship between the Egyptian LSDA isolate obtained in this study and other selected LSDV, GTPV and SPPV strains.
Multiple sequence alignments of deduced amino acids of RNA polymerase 30 kD subunit (RPO30) protein of LSDV. The Egyptian LSDA isolate was aligned with representative LSDV sequences retrieved from GenBank.